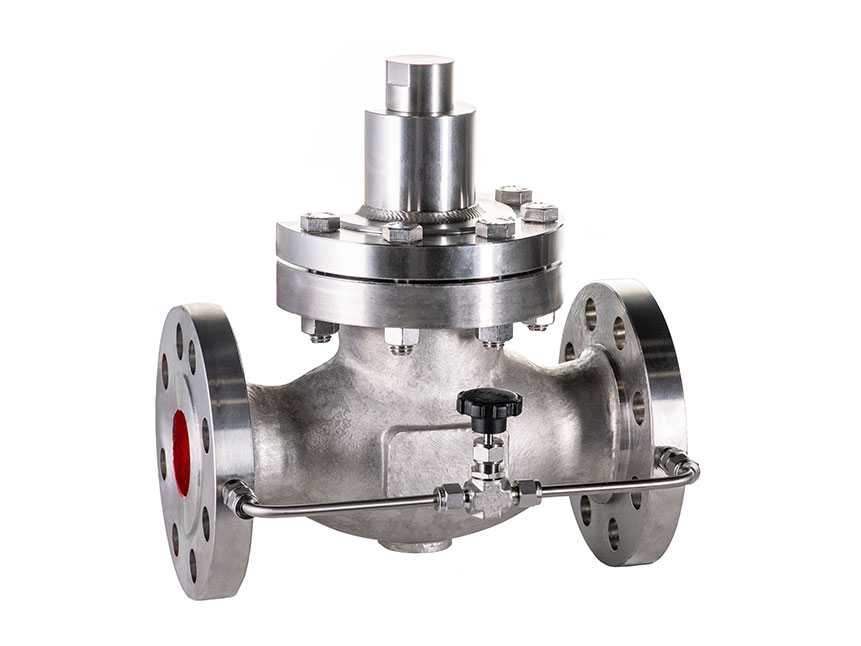
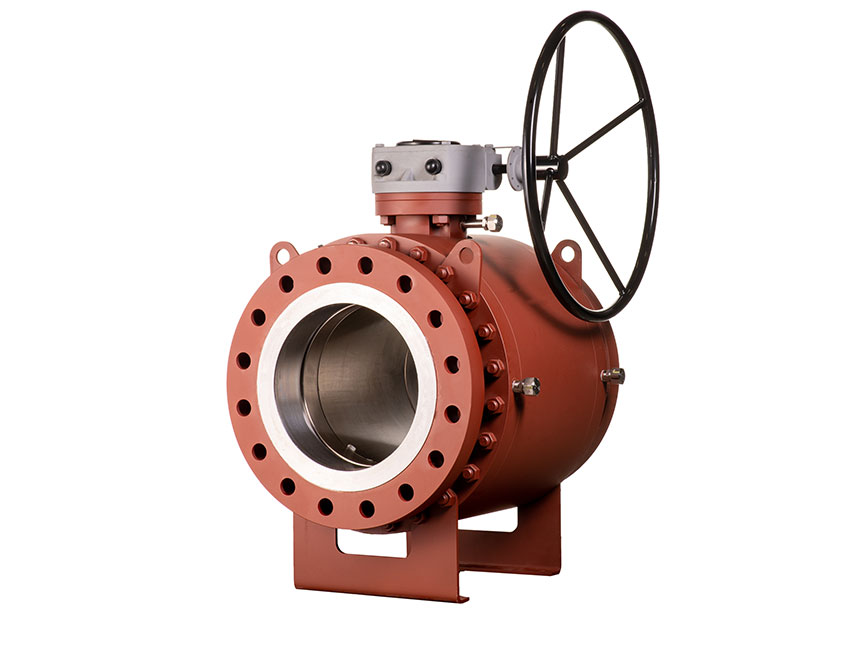
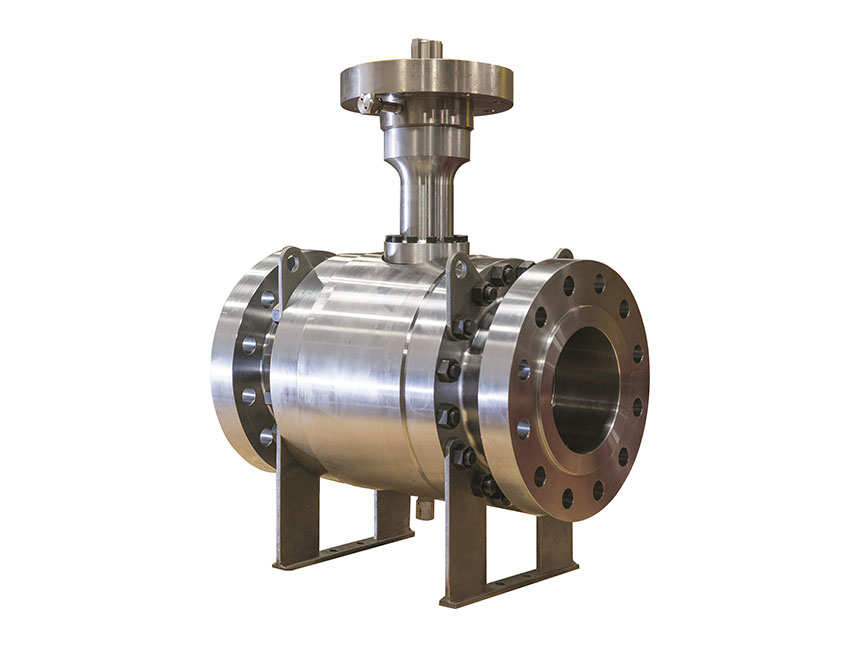
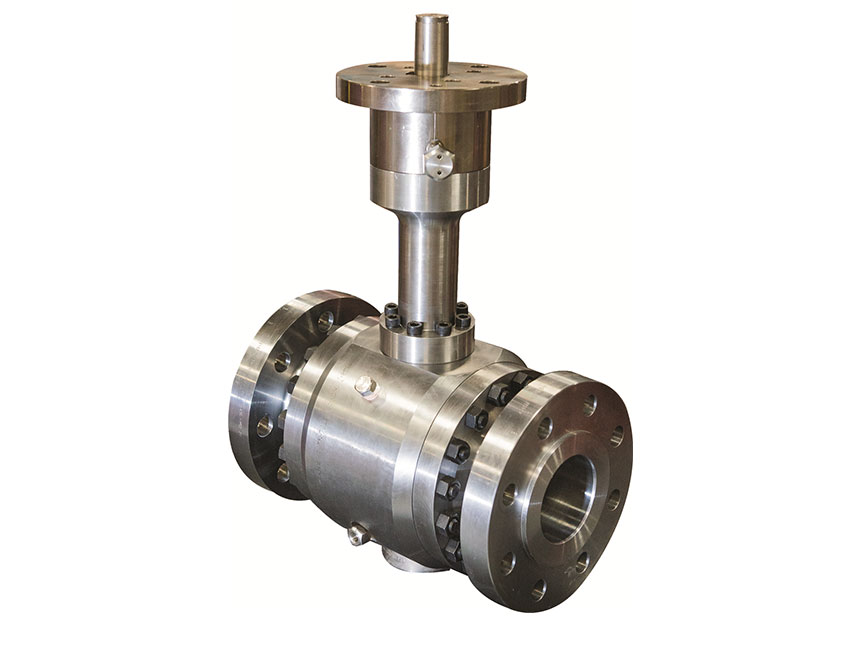
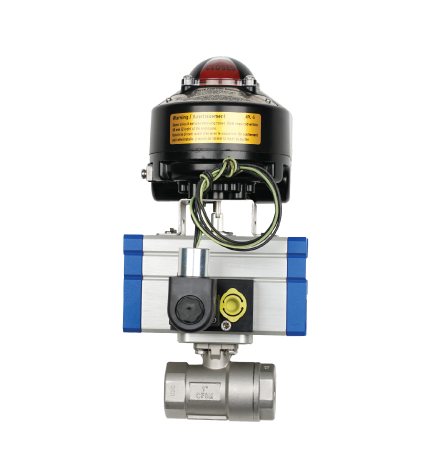
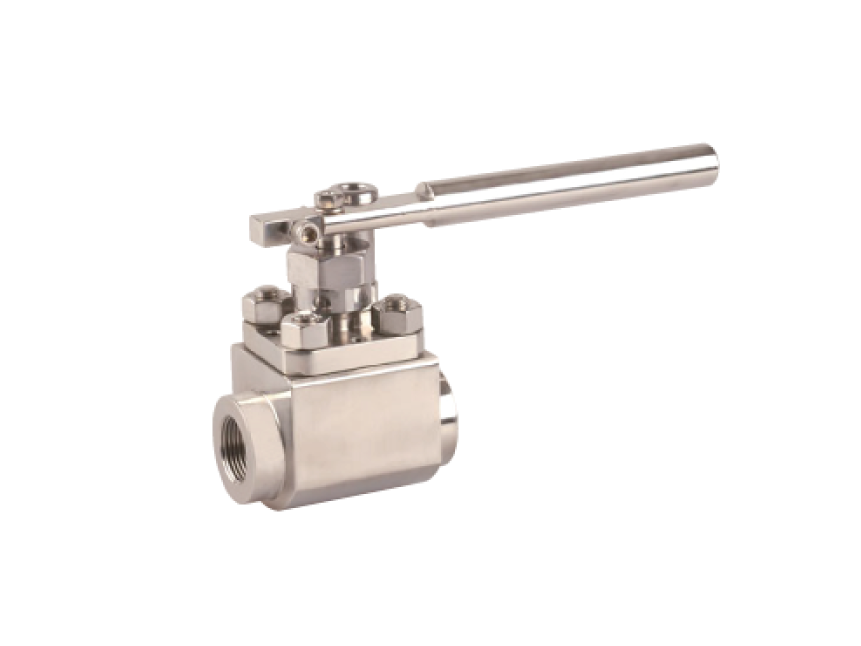
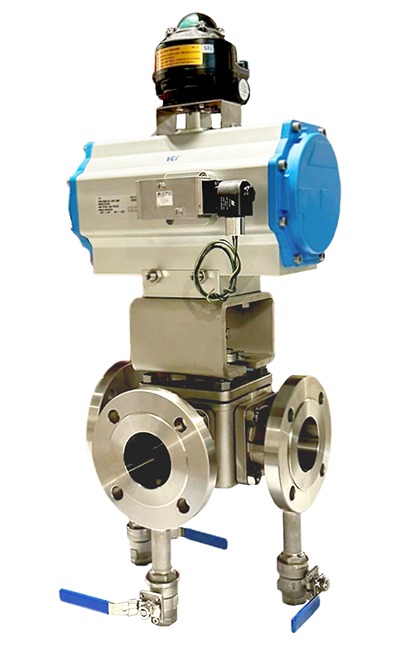
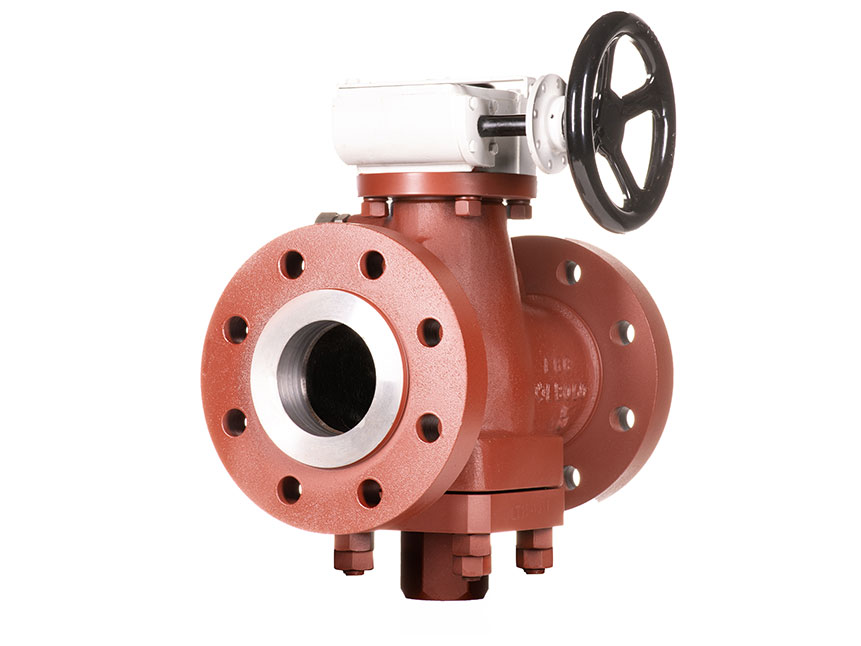
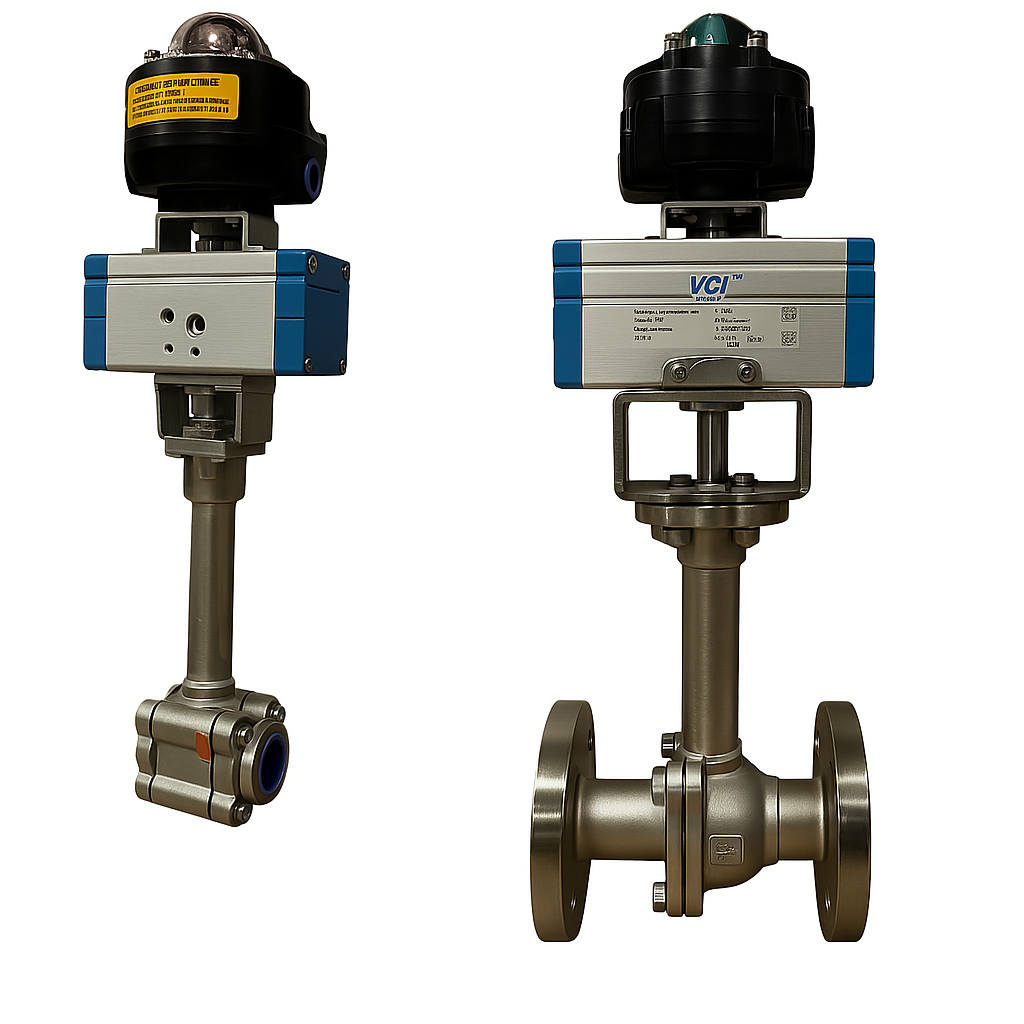
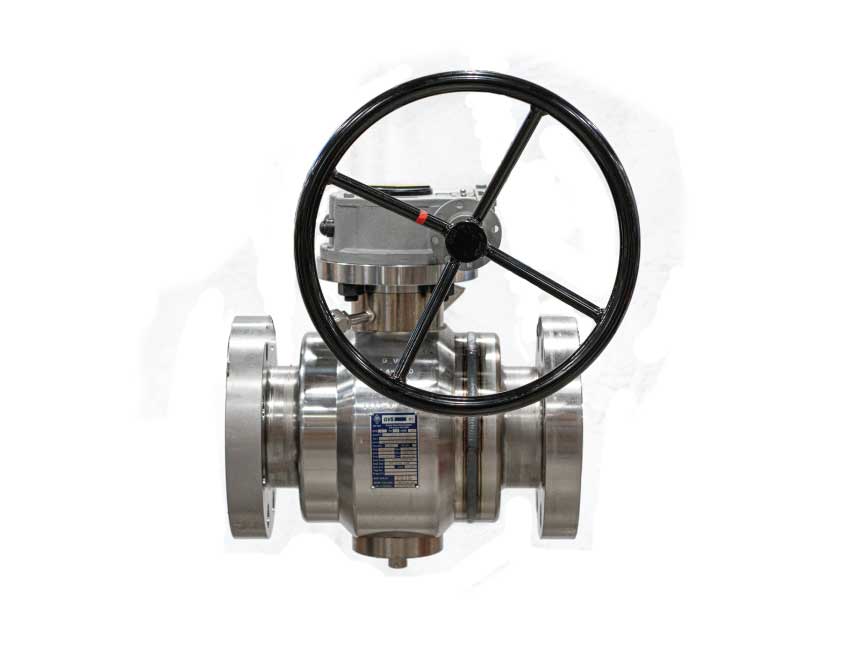
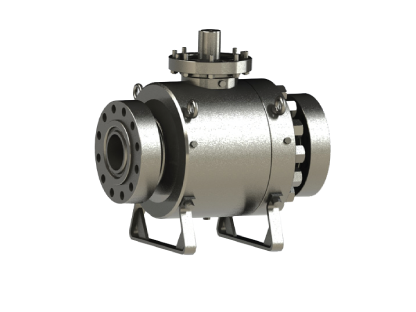
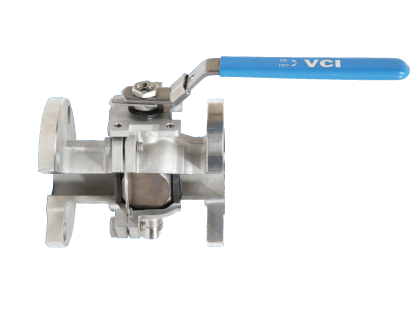
GVS MXF Safety Excess Flow Valves are used in the energy industry to provide automatic shut-off in the event of a sudden flow surge or line rupture, preventing uncontrolled gas or fluid discharge. These valves are commonly installed in fuel gas supply lines, LNG systems, compressed gas networks, and emergency distribution manifolds, where mechanical closure is required without reliance on electricity, air supply, or control systems. Their passive, pressure-differential design makes them ideal for remote installations, off-grid facilities, and critical safety systems where rapid isolation is essential to minimize risk to personnel, equipment, and the environment.
- Fuel Gas Supply Lines: Automatically shut off gas flow in the event of a rupture or downstream line break, protecting combustion systems.
- LNG Systems: Provide mechanical shut-off during rapid discharge or failure in cryogenic transfer lines, preventing hazardous spills.
- Compressed Gas Networks: Serve as passive safety devices that isolate sections of piping during sudden pressure drops or equipment failure.
- Emergency Distribution Manifolds: Ensure safe, immediate flow interruption in critical gas or fluid supply systems without external power.
- Remote Installations: Offer fail-safe protection in off-grid energy sites where electronic or pneumatic actuation is not feasible.
- Turbine Fuel Trains: Prevent excessive fuel discharge in the event of line damage, enhancing fire safety around high-temperature rotating equipment.
The GVS MXF Safety Excess Flow Valve is used in the automotive industry—including the fuel cell manufacturing sector—to provide automatic mechanical shut-off when abnormal flow surges or downstream line failures occur. In traditional automotive production, these valves are installed in compressed air supply lines, CNG and LNG fueling systems, hydraulic testing equipment, and fuel distribution networks to protect systems from catastrophic fluid or gas release. In the fuel cell sector, they are applied in hydrogen supply lines, cryogenic liquid hydrogen transfer systems, and fuel cell test benches, where rapid, fail-safe isolation is critical to prevent hazardous gas release, ensure operator safety, and maintain compliance with stringent hydrogen safety standards.
- Compressed Air Supply Lines: Automatically shut off air flow in the event of a downstream hose failure or sudden rupture to protect tools and operators.
- CNG Fueling Systems: Provide fail-safe closure in compressed natural gas dispensing lines if a hose or coupling failure occurs during vehicle fueling.
- LNG Fueling Systems: Isolate cryogenic LNG transfer lines instantly upon detecting an abnormal flow surge to prevent hazardous release.
- Hydraulic Testing Equipment: Stop fluid flow immediately if a hydraulic line bursts during automotive component or system testing.
- Fuel Distribution Networks: Protect in-plant fuel transfer lines from uncontrolled discharge due to leaks or line breaks.
- Hydrogen Supply Lines (Fuel Cell Production): Rapidly shut off hydrogen flow in production or test environments when a leak or line failure is detected.
- Cryogenic Liquid Hydrogen Transfer Systems: Ensure immediate isolation in LH₂ handling to protect against catastrophic low-temperature gas release.
- Fuel Cell Test Benches: Safeguard test equipment and personnel by stopping hydrogen flow instantly during abnormal operating conditions.